# Promotion Strategy
Integrated marketing communications -> promotion strategy aimed to reach target audience with the desired message.
Consists of three elements: consumer, communication channels, and evaluation of communication results.
# Communicating with Consumers
# Communication Process
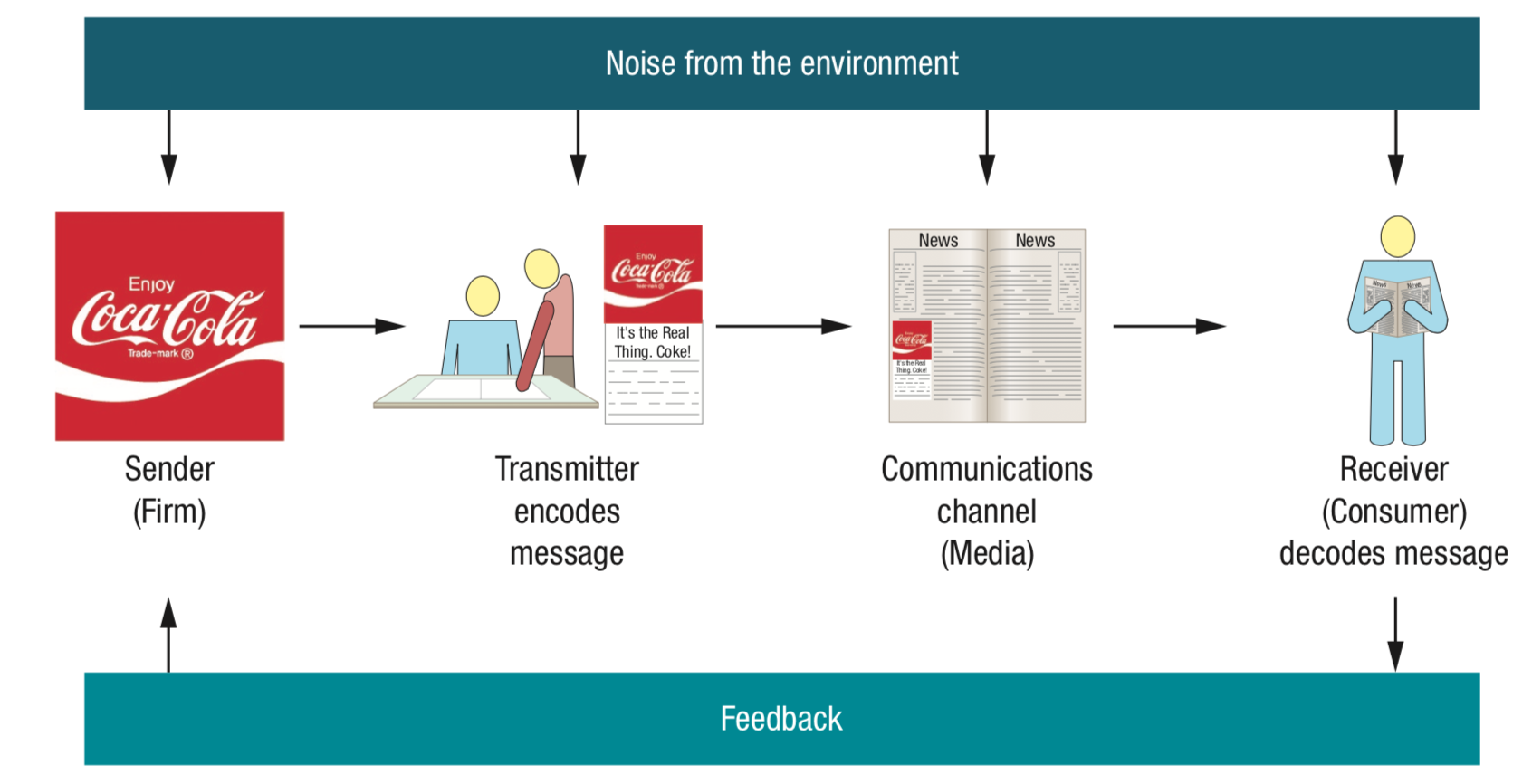
A model that describes how communicates go from a firm to their consumers.
- Sender -> Message originator, must be clearly identified to audiences.
- Transmitter -> A creative department that receives and transforms information.
- Encoding -> Convert ideas into a message. Emphasis on what the consumer receives rather than what is sent.
- Communication channel -> The medium that carries the message.
- Receiver -> The person who reads/hears/sees and processes the information contained in the message.
- Decoding -> Process by which the receiver interpets the message.
- Noise -> Any interference that conflicts with the intended message
- Conflicting messages
- Lack of message clarity
- Flaw in communication medium
- Feedback -> Allows the receiver to communicate with the sender to ensure whether the message was received and decoded correctly
# How Consumers Perceive Communication
- Receivers decode messages differently -> Each receiver decodes the message in their own way and is often not in the way the sender intended
- Senders adjust messages based on the medium and the receiver's traits
# AIDA Model
Marketing communications intend to move consumers through a series of mental stages. The AIDA model is the most popular model to describe these stages.
AIDA model: Awareness -> Interest -> Desire -> Action
# Awareness
Brand awareness refers to a potential customer's ability to recognize the brand and their associated products.
- Aided recall -> When consumers indicate they know the brand when the name is presented to them
- Top-of-mind awareness -> When consumers specifically ask for a brand when purchasing a product
# Interest
Communication must work to increase the interest level of the potential customers.
- Consumers must be persuaded that it is a product worth investigating.
# Desire
Once the firm has piqued interest in the target market, subsequent messages should attempt to move customers from "I like it" to "I want it".
# Action
Goal of communications -> Drive consumer to action.
- Lagged effect -> A delayed response to a marketing communications campaign.
- Typically takes several ad exposures before consumers fully process the message
- Makes it difficult to measure the effectiveness of a campaign
# Promotional Mix
- Advertising -> Placement of announcements and persuasive messages
- Typically requires little action from consumers
- Public Relations -> Management of communications to achieve a variety of objectives including:
- Maintaining a positive image
- Maintain positive relationship with media
- Handling of unfavorable events
- Sales promotions -> Special incentives or excitement-building programs that encourage customers to purchase a product
- Coupons, rebates, contests, free samples, point-of-purchase displays
- Personal selling -> Two-flow communication between a seller and buyer with the intention of persuading the buyer to purchase the product
- Direct marketing -> Direct interaction with customers with the intention of generating a response or transaction
Identify target audience
Can be determining factor in deciding if an advertisement campaign is successful or not.
- Should keep in mind that the target audience may or may not be the current users of the product.
Promotional strategies
- Push strategy -> Increase demand by focusing on wholesalers, retailers, and salespeople.
- Pull strategy -> Get consumers to pull the product into the marketing channel by increasing the demand for it.
Promotional objectives
- Informative -> Create and build brand awareness.
- Often useful for new products or incoming sales events.
- Persuasive -> Motivate consumers to take action.
- Accelerate market's acceptance of product
- Persuade customers to choose your brand over competitors
- Common in growth and early maturity stages of product life cycle
- May be used to reposition an established brand by changing consumer perceptions of the product
- Reminder -> Remind and prompt repurchases.
- Common in maturity stage of product life cycle
Message
- Determine the key message it wants to communicate
- Communicate problem solving ability or unique selling proposition (what differentiates the product from competitors)
- Determine the appeal that would most effectively convey the message
- Information appeals -> Appeal consumers by providing factual information
- Emotional appeals -> Satisfy consumers' emotional desires
# Advertising
Focus of advertisements
- Product-focused -> Aimed at raising awareness of a specific product or service
- Institutional -> Raise awareness of issues related to places, politics, or an industry
- PSAs -> Focus on public welfare, typically sponsored by nonprofit institutions
- Social marketing -> Application of marketing principles to a social issue
Advertising budget
Considerations when determining the advertising budget:
- Role advertising plays in meeting overall promotional objectives
- Varying advertising costs throughout product life cycle
- Nature of market and product
- B2B advertising generally warrants lower costs than B2C
# Public Relations
PR activities often support other promotional efforts by generating free media attention and goodwill.
Public sees media coverage generated by PR as more objective as it is not bought
Cause-related marketing -> Promotion activity where businesses partner with charities to promote a product for their mutual benefit
Key PR Activities
- Publicity -> press releases, interviews, newsletters, etc.
- Sponsorship -> provide support (financially or otherwise) to various activities
- Corporate communications -> annual reports, corporate websites, etc.
- Special events -> open houses, public meetings
- Social media
# Sales Promotions
Special incentives or excitement-building programs that encourage customers to purchase products. Aimed at short-term results.
- Coupons -> Offer discount on the price of specific items when they are purchased
- Deal -> Short term price reduction
- Premium -> Offers an item for free or bargain price as a reward for some type of activity e.g. sampling, buying something else, testing, etc.
- Contest -> Brand-sponsored competition that requires some level of skill or effort
- Sweepstakes -> Offer prizes based on a chance drawing of entrants' names or some other identification
- Samples -> Offer opportunity to try product before they make a buying decision
- Loyalty programs -> Offer premiums or other incentives to returning customers
- Point-of-purchase displays -> Merchandise displays located at point of purchase e.g. checkout counter
- Rebates -> Price reduction in the form of a cashback
- Product placement -> Payment to have a product shown in nontraditional situations e.g. in a movie scene
Drawbacks
- Consumers may stockpile items because of price reduction -> shifting sales from future to present.
- Not a problem for perishable products like groceries
Cross-promoting -> Two or more firms join to reach a specific target market.
- All firms must appeal to the same target market
- Cummulatively create value for customers
# Personal Selling
Value Added
Personal selling is costly so many organizations have chosen to move away from it. Many firms still do however, and that's because the value added outweights the cost:
- Provide information and advice -> Salespeople are knowledgeable and can be good sources of information for customers seeking advice
- Save time and simplify buying
- Build relationships -> Salespeople have the greatest opportunity to build relationships with customers
Personal Selling Process
- Generate and qualify leads
- Generate a list of potential customers (leads) and assess their potential (qualify)
- Ways to discover leads:
- Talk to current customers
- Search on internet
- Networking events
- Inbound marketing -> Drawing attention of customers through online sources
- Trade shows -> Major events attended by buyers who choose to be exposed to a variety of products and services
- Qualify customers
- Do the customer's needs pertain to a specific product or service?
- Do they have the financial resources to pay for the product or service?
- Ways to discover leads:
Pre-approach -> Create a plan for meeting with the customer
Presentation and handling objections -> Assess customer need and determine how the product can attend to this need.
Closing
Follow-up