# Managing Employees' Performance
Performance appraisals are crucial as they provide information to all members of an organization about what they need to succeed.
# Performance Management Process
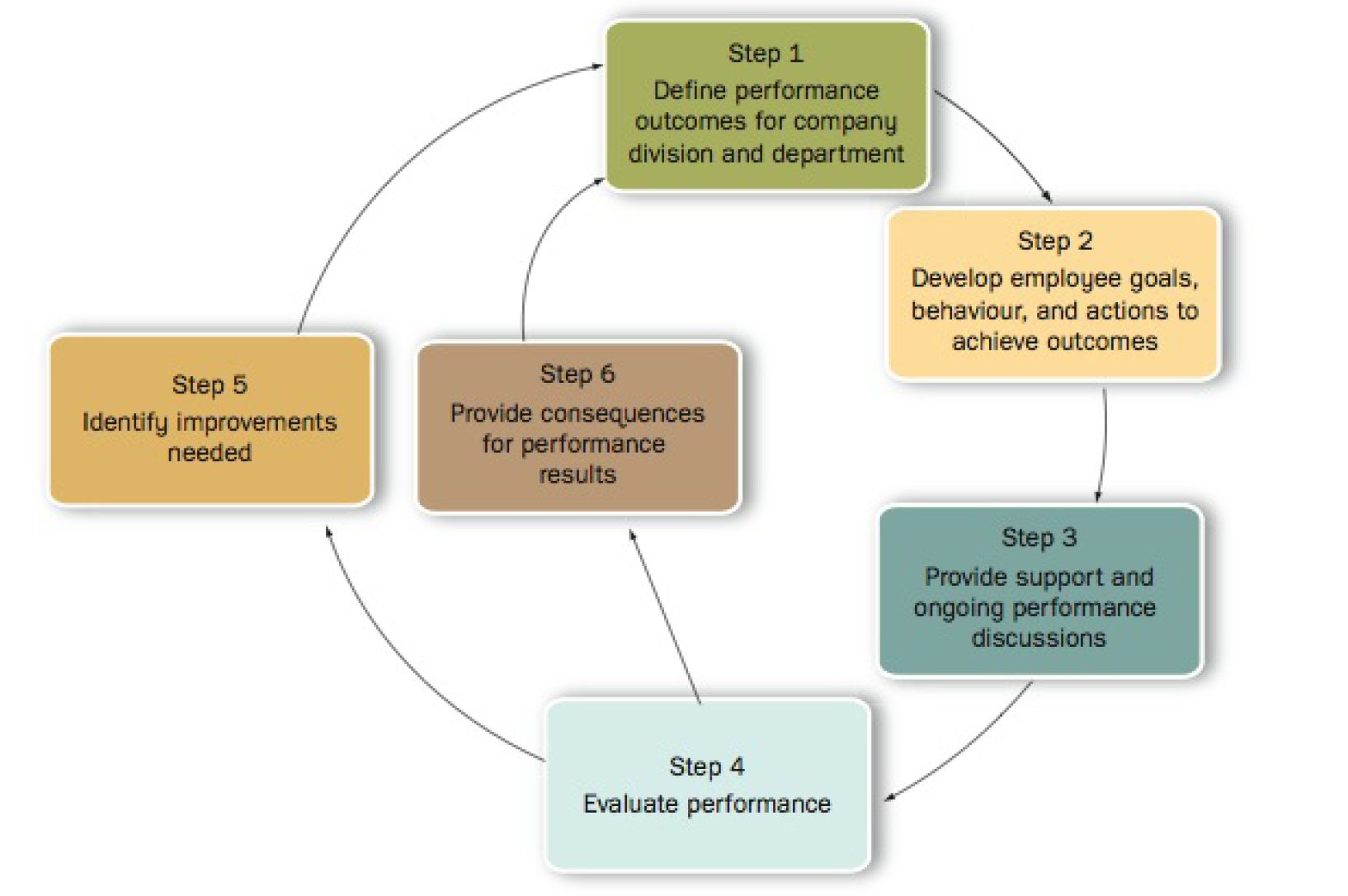
An effective performance management process should contribute to a company's overall competitive advantage.
- Step 1 and step 2: Convert organization goals -> successful employee behaviours
- Step 3: Provide support that allows employee to achieve goals
- Step 4: Performance appraisals
- Step 5 and step 6: Ongoing feedback on improvements on employee behaviour/actions
# Reasons for Conducting Performance Appraisals
- Strategic purpose
- Link organization goals -> employee behaviour
- Communicate goals to employees
- Good employee performance drives company strategy
- Administrative purpose
- Provides information on decisions like pay, salary increases, recognition programs, etc.
- Development purpose
- Basis for developing employee knowledge and skills
- Feedback on areas employee can improve on
# Criteria for Effective Performance Management
Fit with strategy — Performance management should aim at achieving employee behaviour and mindset that fits with the organization's strategy.
- If a company emphasises customer service, then the performance management should emphasise the behaviour that contribute to excellent performance.
Validity — Does the performance appraisal measure all relevant aspects of performance?
- Contamination -> irrelevant collected information
- Deficiency -> relevant information that is not considered
Reliability — Describes the consistency of the results that the performance measure will deliver.
Acceptability — The people who use the performance measure must deem it acceptable. If management sees it as time-consuming, they will not use it. Likewise, if employees believe the measure is unfair, they will not use the feedback.
Specificity — A performance measure should specifically tell employees what is expected of them and how they can meet those expectations.
# Performance Appraisal Process
- Define performance expectations
- Create expectations based off job analysis and description
- Communicate expectations to employees
- Appraise performance
- Provide feedback
# Performance Measurement Methods
Step 2 in performance appraisal process. Performance is generally measured with regards to one of three options:
- Traits
- Checks degree to which employees posses specific characteristics
- May not have correlation to productivity
- Behaviours
- Emphasizes how employees complete tasks
- Results
- Emphasizes what employees complete
Many organizations choose to determine performance through a ranking system where employees are directly compared to each other.
# Ranking
- Simple ranking -> Managers rank each employee from highest-performer to lowest-performer.
- Alternation ranking -> Managers alternatingly rank employees; pick highest performer, then lowest performer, then second highest, etc.
- Forced-distribution -> Group certain proportions of employees into a pre-defined set of categories.
- Good if employees truly have high spread in performance
- Poor or unfair if employees are generally level
- Paired-comparison -> Compares employees with each other to establish rankings
Ranking is generally good because:
- Removes tendency to rank everyone in the "center" of the distribution
- Removes biases caused by a manager being too lenient or too strict
- Useful for making decisions on pay/layoff distribution
Notable drawbacks:
- Difficult to link back to organization goals
- Provides non-specific feedback to employees
- Unfair if employees are all high performers
# Traits
- Graphic rating scale
- List a series of attributes with respective rating scales
- Manager uses scale to indicate extent in which employee satisfies the attritubes
- Low reliability -> up to manager's discretion as to what defines "outstanding expectations", "meets expectations" etc
Attribute-based performance methods are generally:
- Easy to implement and use -> most popular used method currently
- Can be reliable and valid if careful consideration on what attributes lead to high performance
- Often not the case
- Difficult to link to strategic goals
- Poor feedback -> employees won't know where or how to improve if they only receive a number in their appraisal
# Behaviours
- Critical incident -> performance measure based on manager's records on employee behaviour that exhibits good/bad performance
- Specific feedback on employee improvements
- Inefficient as a comparison metric
- Behaviourally anchored rating scale (BARS) -> scale of behaviour "anchors" that describes what behaviours correlate to what level of performance
- High validity -> job related behaviours
- High feedback -> very specific on required behavioural changes
- Time consuming
- Requires tailoring for every job
Organizations may implement organizational behaviour modification -> plan of behaviour management through a formal system of feedback and reinforcement.
# Results
- Productivity (output)
- Determine desired outcome -> determine method to measure the outcome -> determine what level of outcome correlates to which level of performance
- Set up system to track these measures while employees complete tasks
- Time consuming but has evidently shown to increase productivity
- Management by objectives (MBO)
- Set goals that "trickle down" -> all employees contribute to goals
- Goals become basis for performance management
- Time consuming
- Inefficent as a comparison measure -> how can an employee be better than another if they contribute to the same final objective?
# Errors in Performance Measurement
# Rating Errors
- Similar-to-me -> tendency to give higher evaluation to individuals that are similar to oneself
- Contrast -> comparing individuals to other employees rather than to objective standard
- An employee might seem weaker if colleagues are outstanding, even if said employee performs job up to standard
- Distribution errors -> tendency to group employees to a particular part of distribution
- Leniency/strictness error -> tendency to rate individuals too high/too low
- Central tendency -> rate all employees somewhere in the middle
- Recency emphasis -> judge solely on most recent work
- Recent poor performance may undermine exceptional historical performance
- Focus-on-activities -> rate based on how busy they appear
- Halo and horns
- Halo -> rank positively in all aspects because employee is exceptional in one aspect
- Horns -> opposite of halo
- Appraisal bias -> allow external characteristics other than performance to influence rating
# Avoiding Rating Errors
- Train raters on common rating errors
- Frame of reference training
- Identify and eliminate errors based on practice e.g. videos, simulations
- Effective but costly and time consuming
- 3rd party review on rating
- Raters are evaluated on how well they do performance appraisal
- Feedback is provided on how raters can minimize errors
# Performance Feedback
Ineffective appraisal can undermine employee performance and contribute to poor work motivation/productivity.
# Scheduling Feedback
- Norm is to provide feedback annually
- Missed improvement opportunity -> if manager notices problem in June, but feedback in November, June -> Nov missed chance to improve
- Feedback most effective when employee not surprised; employee shouldn't wait for a year to know what their manager thinks of their work
# Preparing Feedback
- Manager should provide neutral setting for meeting
- Ask employee to do a self-assessment
- Potentially provide meaningful discussion if a gap occurs between manager and employee's ratings
# Conducting Feedback
Three approaches:
- Tell-and-sell -> management provides ratings then justify ratings
- Tell-and-listen -> management provides ratings then allow employee to justify those ratings
- Problem solving -> management and employee work together to come up with solutions to performance issues
General principles:
- Feedback should paint balanced and accurate picture of employee performance
- Should show specific areas of improvement
# Performance Improvement
Feedback should indicate what employees can do to improve their performance. The "what" is based on what attribute the employee is missing (either motivation or ability).
- Lack of ability -> provide training or restructure job to suit their ability.
- Lack of motivation -> ensure employee is being treated fairly and rewarded adequately.
- Sometimes may be as simple as lack of positive reinforcement.
- Lack of both -> employee may not be suited for position.
Generally employees with high motivation and high ability perform best.